命令模式
命令模式(Command Pattern)是一种行为设计模式,它将请求封装为对象,从而使你能够参数化客户端发出的请求、排队请求、记录请求日志、支持可撤销的操作等。命令模式的关键是将“动作的请求”与“动作的执行”分离开来,这样可以在不同的时间点指定、配置和执行请求。
类图
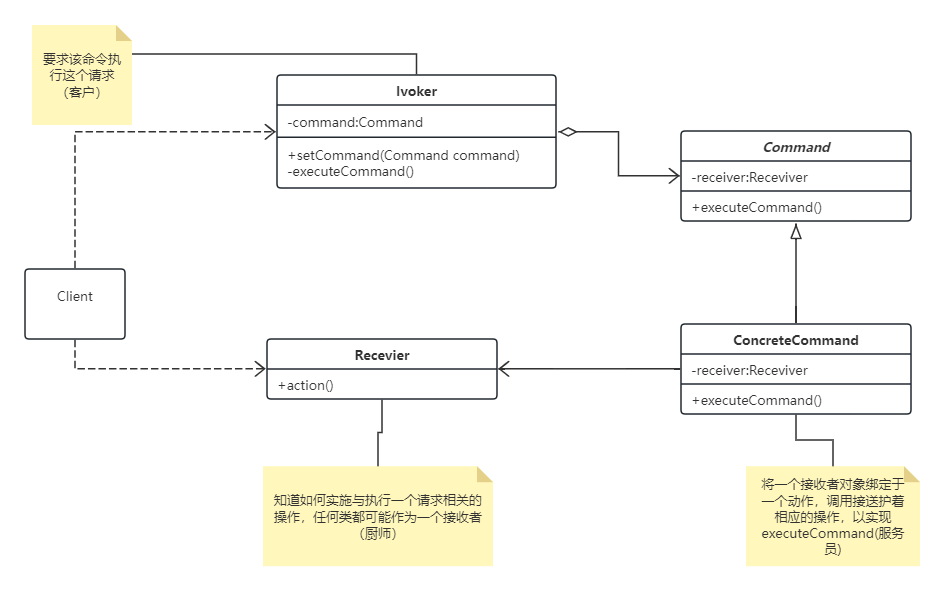
主要角色
- Command(命令接口):定义所有命令的公共接口,通常包含一个
execute()方法。 - ConcreteCommand(具体命令):实现命令接口,负责调用接收者的相关方法来执行具体操作。
- Receiver(接收者):真正执行命令中所描述操作的类。它知道如何根据命令执行相关的业务逻辑。
- Invoker(调用者/请求者):发起命令的对象,它并不知道命令的具体执行细节,只是持有命令对象并调用其execute()方法。
优点
《大话设计模式》
- 容易地设计一个命令队列
- 在需要的情况下,可以容易地将命令记入日志
- 允许接受请求的一方决定是否要否决请求
- 可以容易地实现对请求的撤销和重做
- 由于加进新的具体命令类不影响其他的类,因此增加新的具体命令类很容易
- 把请求一个操作的对象与知道怎么执行一个操作的对象分割开
缺点
- 可能导致类的膨胀:增加新的命令需要编写新的命令类,可能导致类的数量增加。
适用场景
任务队列或请求排队
在需要对任务或请求进行排队处理的场景中,命令模式非常适用。例如,打印队列中的打印请求、网络请求的异步处理等。使用命令模式可以将每个请求封装成一个命令对象,然后将这些对象添加到队列中按顺序执行。
宏命令(宏操作)
在需要组合一系列操作为一个操作的场景中,命令模式非常有效。例如,应用程序中的“撤销”和“重做”功能,或复合命令(如在图形编辑器中实现多个图形操作的组合)。
实现日志请求
命令模式可以用于记录系统中的所有操作,以便在系统崩溃时重做操作。例如,数据库事务日志、操作系统的命令日志等。
支持撤销操作
在需要支持撤销和重做功能的应用中,命令模式非常有用。例如,文本编辑器、图形编辑器、IDE等。通过将每个操作封装为命令对象,可以轻松实现撤销和重做功能。
参数化对象
命令模式可以用于将操作参数化。例如,在菜单项和按钮上执行不同的操作,通过将命令与这些控件关联,可以使得每个控件执行不同的操作,而不需要改变控件本身。
多层级的命令处理
在复杂的系统中,可能需要将命令分发到不同的处理层。命令模式可以帮助实现这一点,例如在游戏开发中,不同的命令可能需要发送到不同的模块(如渲染模块、物理引擎模块等)。
GUI中的命令处理
在图形用户界面(GUI)应用中,每个按钮、菜单项都可能对应一个具体的操作。通过命令模式,可以将这些操作封装成命令对象,按钮和菜单项只需调用这些对象的执行方法即可。例如,Java的Swing框架中广泛使用了命令模式。
示例
package com.justin.command.light;
import java.util.Stack;
//命令接口
interface Command {
void execute();
void undo();
}
//具体命令
class LightOnCommand implements Command {
private Light light;
public LightOnCommand(Light light) {
this.light = light;
}
@Override
public void execute() {
light.on();
}
@Override
public void undo() {
light.off();
}
}
class LightOffCommand implements Command {
private Light light;
public LightOffCommand(Light light) {
this.light = light;
}
@Override
public void execute() {
light.off();
}
@Override
public void undo() {
light.on();
}
}
//接收者
class Light {
public void on() {
System.out.println("The light is on.");
}
public void off() {
System.out.println("The light is off.");
}
}
//调用者
class RemoteControl {
private Command command;
private Stack<Command> history = new Stack<>();
public void setCommand(Command command) {
this.command = command;
}
public void pressButton() {
command.execute();
history.push(command);
}
public void pressUndo() {
if (!history.isEmpty()) {
Command lastCommand = history.pop();
lastCommand.undo();
}
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Light livingRoomLight = new Light();
Command lightOn = new LightOnCommand(livingRoomLight);
Command lightOff = new LightOffCommand(livingRoomLight);
RemoteControl remote = new RemoteControl();
remote.setCommand(lightOn);
remote.pressButton(); // 输出: The light is on.
remote.pressUndo(); // 输出: The light is off.
remote.setCommand(lightOff);
remote.pressButton(); // 输出: The light is off.
remote.pressUndo(); // 输出: The light is on.
}
}下面是一个更复杂的例子,展示了一个文本编辑器应用如何使用命令模式实现撤销和重做功能
命令接口和具体命令:定义了 execute 和 undo 方法。
public interface Command {
void execute();
void undo();
}
public class AddTextCommand implements Command {
private TextEditor editor;
private String text;
public AddTextCommand(TextEditor editor, String text) {
this.editor = editor;
this.text = text;
}
@Override
public void execute() {
editor.addText(text);
}
@Override
public void undo() {
editor.deleteText(text.length());
}
}
public class DeleteTextCommand implements Command {
private TextEditor editor;
private int length;
private String deletedText;
public DeleteTextCommand(TextEditor editor, int length) {
this.editor = editor;
this.length = length;
}
@Override
public void execute() {
deletedText = editor.getText().substring(editor.getText().length() - length);
editor.deleteText(length);
}
@Override
public void undo() {
editor.addText(deletedText);
}
}接收者(Receiver)TextEditor 类,它包含具体的操作方法 addText 和 deleteText。
public class TextEditor {
private StringBuilder text = new StringBuilder();
public void addText(String newText) {
text.append(newText);
}
public void deleteText(int length) {
int start = text.length() - length;
if (start >= 0) {
text.delete(start, text.length());
}
}
public String getText() {
return text.toString();
}
}调用者:CommandInvoker 类,它管理命令的执行和撤销。
客户端:创建具体命令对象,将接收者传递给命令对象,并通过调用者执行和撤销命令。
import java.util.Stack;
public class CommandInvoker {
private Stack<Command> commandHistory = new Stack<>();
public void executeCommand(Command command) {
command.execute();
commandHistory.push(command);
}
public void undoLastCommand() {
if (!commandHistory.isEmpty()) {
Command lastCommand = commandHistory.pop();
lastCommand.undo();
}
}
}
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TextEditor editor = new TextEditor();
CommandInvoker invoker = new CommandInvoker();
// 添加文本
Command addHello = new AddTextCommand(editor, "Hello ");
invoker.executeCommand(addHello);
Command addWorld = new AddTextCommand(editor, "World!");
invoker.executeCommand(addWorld);
System.out.println(editor.getText()); // 输出: Hello World!
// 撤销添加 "World!"
invoker.undoLastCommand();
System.out.println(editor.getText()); // 输出: Hello
// 撤销添加 "Hello "
invoker.undoLastCommand();
System.out.println(editor.getText()); // 输出: (空字符串)
}
}